Disclosure of climate-related information based on TCFD’s recommendations
In December 2021, Taikisha expressed its support for the recommendations of the “Task Force on Climate-related Financial Disclosures (TCFD)” and joined the “TCFD Consortium.” The mitigation of and adaptation to climate change is one of our top management priorities (materialities), and we are endeavoring to reduce environmental impacts through our core business of providing air conditioning and sanitation equipment, and painting plants with high energy-saving performance.
In addition, in order to identify and evaluate climate-related risks and opportunities and to understand the medium to long-term impacts of climate-related issues on our businesses, we conducted scenario analyses of two businesses, the green technology system and paint finishing system. Based on the results of these analyses, we disclose climate-related information in line with TCFD’s recommendations.
Governance
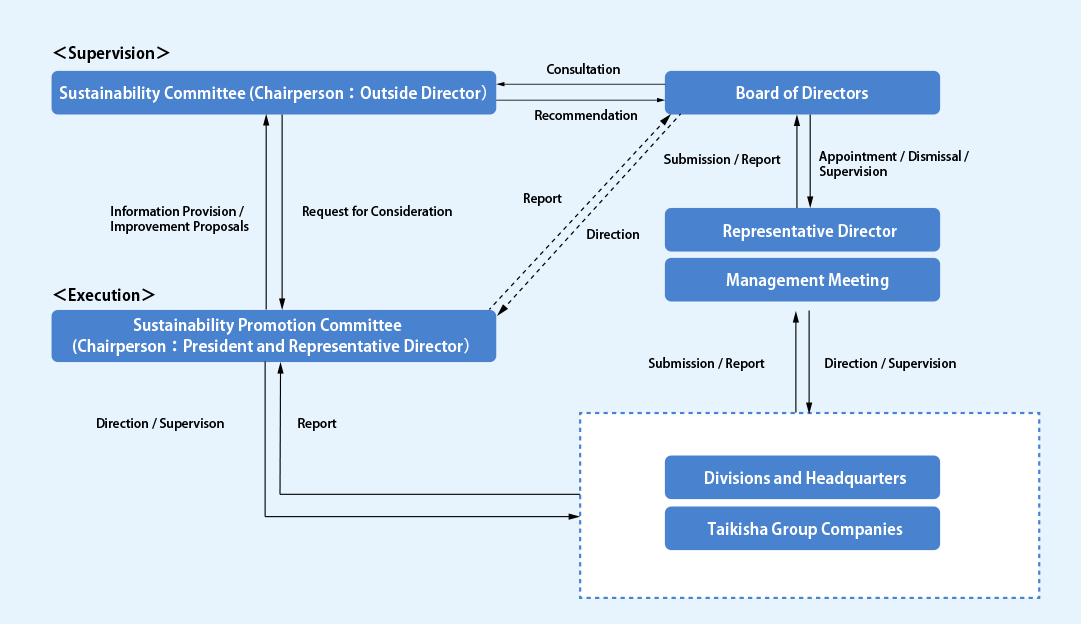
The Company has established the Sustainable Committee, which is an advisory body of the Board of Directors, with an aim of strengthening our efforts to address social issues, including climate change, from the perspective of the realization of sustainable society and perpetual corporate growth. The Sustainable Committee is chaired by an Outside Director and consists of 9 members, namely 4 Outside Directors including the chairperson and 5 Executive Directors. The Sustainable Committee replies to questions from the Board of Directors, and makes proposals or recommendations to the Board of Directors.
In addition, the Company has established the Sustainable Promotion Committee as an executive body on the executive side that acts on the basis of resolutions, etc. of the Board of Directors. The Sustainable Promotion Committee consists of 5 Executive Directors including the Representative Director, President as chairperson, and responsible person for sales department of each business division, and which discussed and implements measures for addressing sustainability issues.
Responsibilities for evaluating and controlling climate-related risks and opportunities are assigned to the President and Representative Director, who chairs the Risk Management Committee. With regard to the linkage with incentives, non-financial indicators are introduced at a specific rate as an evaluation factor to the compensation structure of the Executive Directors, encouraging the strengthening of promotional activities.
Strategies
In order to identify and evaluate climate-related risks and opportunities and to understand their impacts on our businesses, we conducted scenario analyses of the Green Technology System Division and Paint Finishing System Division through the process described below.
Specifically, we firstly identified factors of risks and opportunities having a great impact on us. Next we conducted an analysis concerning shifts in policies and market trends, and physical changes attributable to disasters, using each of a less-than-2°C scenario, which assumes that the average temperature rise of the world in FY 2035 will be kept below 2°C, and a 4°C scenario, which assumes that the average temperature will rise by approximately 4°C. We perceived “carbon taxes,” “changes in customer behavior,” and “prevalence of energy-saving and renewable energy technologies” as shift factors, and “average temperature rise” as a physical factor, and identified them as important risks and opportunities.
The degrees of the financial impacts on the businesses verified in each scenario are indicated in units of one billion yen using arrows, and a countermeasure against each of the impacts is also described.
Analysis process
-
Evaluation of the degree of the priority of each risk
Identify the risks and opportunities of climate change that Taikisha Group is currently confronted with and is expected to be confronted with in the future in the Green Technology System Division and Paint Finishing System Division, and evaluate their degrees of importance on our future businesses.
-
Definition of scenarios
Select multiple scenarios, and then obtain objective future information on parameters related to risk and opportunity items. Based on this information, categorize global movements around us, including the behavior of future stakeholders in each of the scenarios.
-
Evaluation of impacts on businesses
Based on global movements in each scenario, consider what strategic options we should take, clarify the gap between existing management, business strategies, and plans and them. Then estimate their impacts on businesses.
-
Definition of countermeasures
Based on each scenario and our actions, scrutinize applicable and realistic countermeasures to address the identified risks and opportunities.
Selected climate change scenarios
With reference to the climate change scenarios published by the International Energy Agency (IEA) and other organizations, we selected the less-than-2°C scenario and the 4°C scenario. With awareness that the impacts of climate change have the nature of becoming apparent over the medium to long period, we analyzed the impacts of climate change in 2035 as the reference timeline.
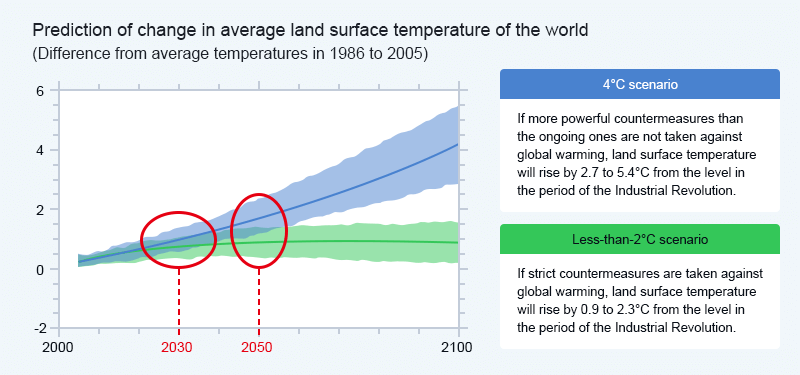 Created by Taikisha based on IPCC AR5 Climate Change 2014 Synthesis Report Summary for Policymakers
Created by Taikisha based on IPCC AR5 Climate Change 2014 Synthesis Report Summary for Policymakers(Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science and Technology, Ministry of Economy, Trade and Industry,
Japan Meteorological Agency, Ministry of the Environment)
Definition of scenarios
A logic tree was used to organize the flow in which the impact of climate change becomes apparent.
Although it is difficult to predict climate change that will occur in the timeline of a medium to long period, we consider it is important to discuss its impacts on our businesses and countermeasures to the maximum extent and flexibly deal with them.
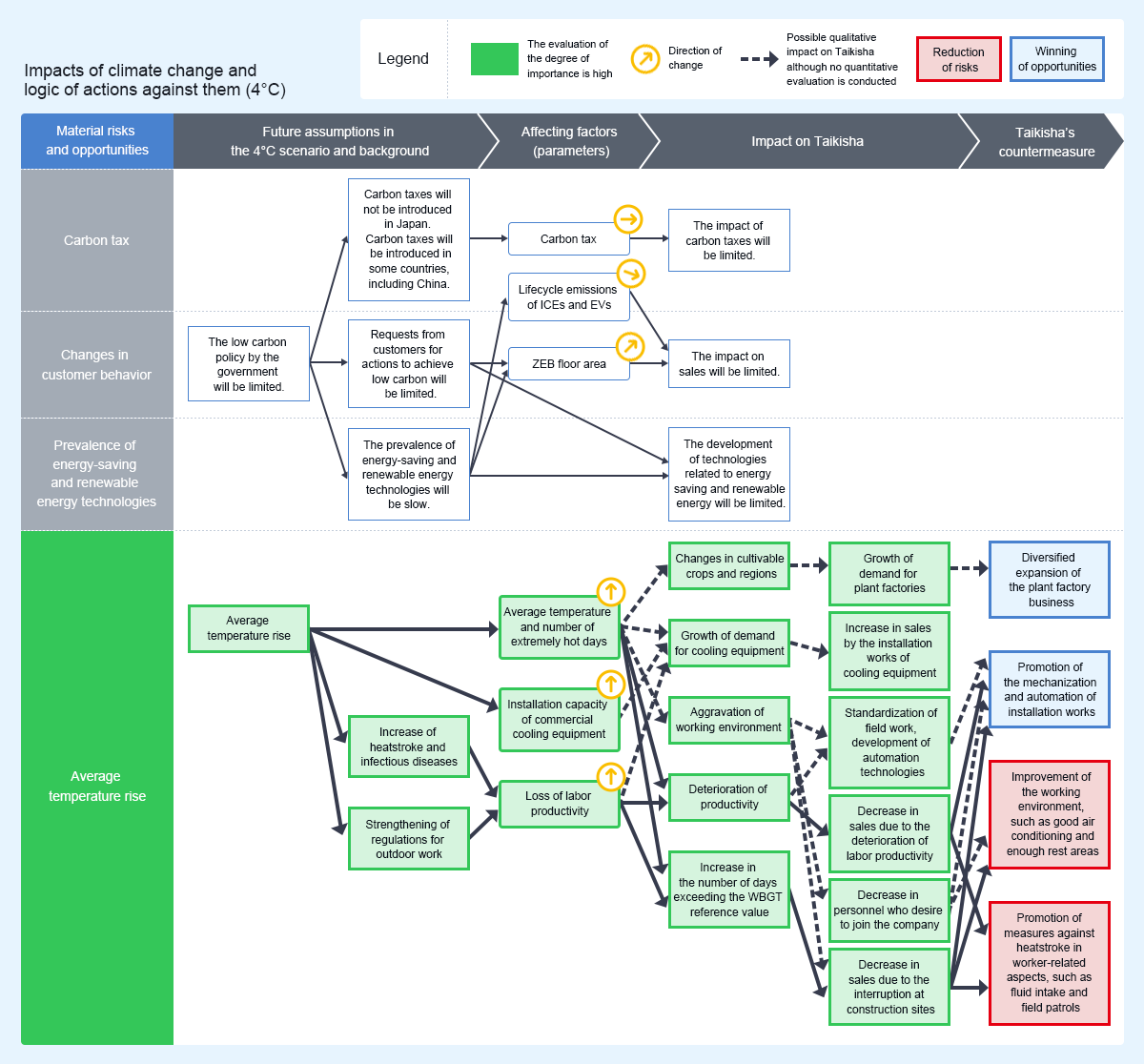
<Assumed 4°C scenario> Green Technology System Division, Paint Finishing System Division
The low carbon policies by the government are limited, and the extent of the transition to a low carbon society will be limited while an average temperature rise will magnify heat stress and the risk of natural disasters. They are expected to have the following impacts on our businesses:
Since it is assumed that carbon taxes will not be introduced in Japan, the impact of increases in material costs due to the introduction of carbon taxes will be limited. When it comes to each divisions demand for net zero energy buildings (ZEBs) will increase in the Green Technology System Division, and demand for energy-saving design plants will grow in the Paint Finishing System Division. However, it is assumed that the impact of requests from customers for actions to achieve low carbon on sales will be limited. On the other hand, as average temperature rises, it will be necessary to capture demand for plant factories and air conditioning systems, and to strengthen countermeasures against heatstroke and infectious diseases at construction sites.
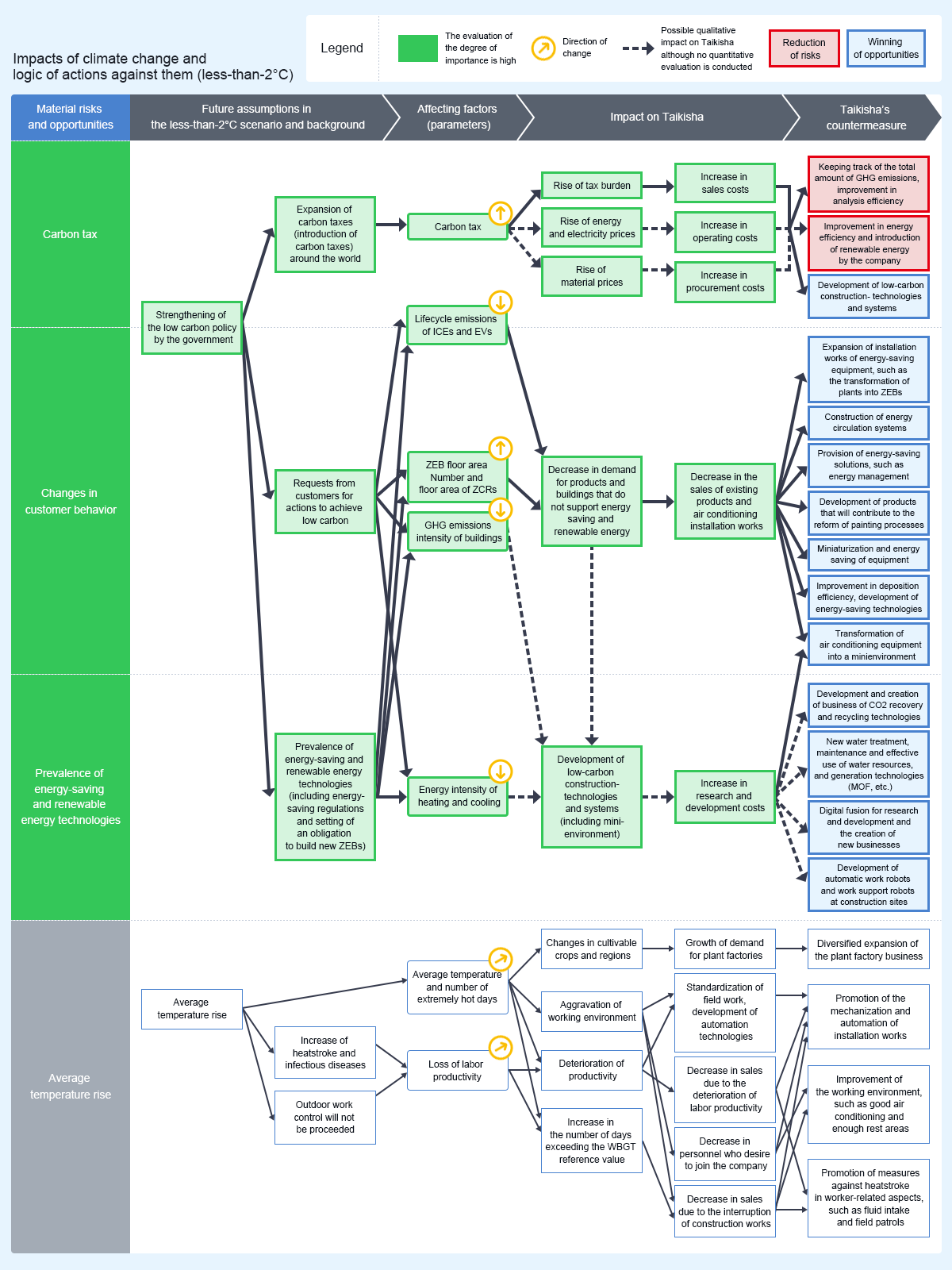
<Assumed less-than-2°C scenario> Green Technology System Division, Paint Finishing System Division
The impacts of physical risks will remain limited, but it will be necessary to deal with transition risks, including various regulations and customer requests. They are expected to have the following impacts on our businesses: It is anticipated that the strengthening of the low carbon policy by the government will incur the impacts burdening us with carbon taxes and increases in material costs, and operating costs will increase. Taking a closer look at these impacts in each business, in the Green Technology System Division, the sales of installation works of existing air conditioning systems will decrease due to stronger requests from customers for actions to achieve low carbon, energy-saving regulations, and the setting of an obligation to build new ZEBs, and for other reasons, but sales are expected to increase as a result of developing products and technologies capable of fulfilling these requests, etc. In the Paint Finishing System Division, demand for painting processes producing less carbon will escalate, and the sales of existing products not supporting low carbon and energy saving will decline, but sales are expected to increase as a result of developing products and technologies designed to support them.
Results of scenario analyses
As a result of the scenario analyses, the material climate-related risks that will affect our businesses, opportunities, and the financial impacts as of FY 2035 are as follows:

| Items of material risks and opportunities | Risk | Opportunity | Financial impact in each scenario | Assumed countermeasure | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 4°C | less-than-2°C | ||||||
| Transition risk, opportuni-ties |
Policy/ Regulation |
Carbon tax |
Introduction of carbon taxes (Due to the rises in carbon prices and material costs, the cost will increase by about 300 million yen in the 4°C scenario and by about 9 billion yen in the less-than-2°C scenario.) |
Growth of demand for low-carbon buildings Increase in sales Growth of demand for low-carbon painting plants (increase in sales) |
|
||
| Industry/ Technology/ Market |
Changes in customer behavior, prevalence of energy-saving and renewable energy technologies | Response to requests from customers (rise of costs and inadequate responses decrease in sales), deterioration of competitiveness in the development of energy-saving and renewable energy technologies (decrease in sales) |
Increase of about 1.1 billion yen in sales in the 4°C scenario and of about 2.2 billion yen in the less-than-2°C scenario as a result of integrating customers’ needs for low-carbon buildings and fluctuations in demand for construction works of growing ZEBs, development of advanced energy-saving and renewable energy technologies (increase in sales) |
|
|||
| Physical risks and opportuni-ties |
Chronic | Average temperature rise |
Deterioration of labor productivity due to an average temperature rise and suspension of construction works due to the increase of extremely hot days (increase of about 400 million yen in operating costs in the 4°C scenario and of about 370 million yen in the less-than-2°C scenario) Revision of labor laws and regulations (decrease in sales) |
Growth of demand for air conditioning system technologies (increase in sales) Promotion of the mechanization and automation of installation works (increase in sales) Growth of demand for plant factories (increase in sales) |
|
||
Risk Management
The Taikisha Group is endeavoring to reduce material risks, including climate change, and minimize risks that will become apparent. The Risk Management Committee assesses the level of each risk, selects risks we should deal with, and formulates and implements policies, for reducing risks from the overall perspective of the group.
Specifically, we have established the Risk Management Rules and organized the Risk Management Committee based on the rules to conduct centralized, effective, and efficient management of the group’s risks. The Committee, chaired by the President and Representative Director, is held twice a year and whenever necessary, and establishes and thoroughly disseminates basic policies, responsibility systems, and operation for company-wide risk management.
When it comes to material risks, including climate change, each of the departments in charge identifies items and determines the “degree of risk (degree of importance)” with three levels - High, Medium, and Low - taking into account the “impact on management” and the “frequency of occurrence.”
Among them, High items that have a significant impact on our strategies or financial status are selected as risks that should be preferentially dealt with and reported to the Risk Management Committee after formulating priority management policies and targets.
The Risk Management Committee assesses the degree of each risk and discusses the priority management policies and targets from a company-wide, comprehensive perspective, and formulates basic policies. Then, each department in charge monitors the progress of its activity plan and reports the results to the Risk Management Committee.
The Chairperson (President and Representative Director) of the Risk Management Committee scrutinizes the status of company-wide risk management and reports it to the Board of Directors twice a year after discussion by the Internal Control Committee.
In addition, the Management Committee, which determines important management matters on the whole, discusses the risks and opportunities of climate change, reviews climate change scenarios, and reflects them in long-term strategies. The Management Committee reports related issues, including the risks of climate change, concurrently with the reporting to the Risk Management Committee.
In order to strengthen risk assessments from a company-wide, comprehensive perspective, the members of the Internal Control Committee conduct additional company-wide assessments and formulate policies.
Indicators and Targets
In order to manage climate-related risks and opportunities, various measures are implemented by setting not only GHG emissions but also indicators, such as energy consumption, water usage, and waste emissions.
Reduction target
In order to evaluate and manage the impact of climate change on its operations, the Group has set a GHG emissions reduction target in its Medium-Term Business Plan, utilizing CO2 emissions in business activities as a key indicator. Additionally, in 2024, the Group reset its target with a view toward obtaining SBT* accreditation, aiming for further reduction in GHG emissions going forward.
-
※SBT:Stands for Science-Based Targets, which refers to GHG emissions reduction targets that are aligned with the levels required by the Paris Agreement.
CO2 emissions in the business activities
- Scope 1 and 2
- 42% reduction by 2030 (vs FY2022 levels)
- Scope 3
- 25% reduction by 2030 (vs FY2022 levels)
SBT accreditation
The Taikisha Group's greenhouse gas emission reduction targets were certified by SBTi (Science Based Targets Initiative) as science-based targets in November 2024. From this point forward, we will develop technologies and proactively promote proposals to our customers to help SBT accreditation reduce CO2 emissions during the operation stage of equipment designed and constructed by our Group. Additionally, we will contribute to the realization of a decarbonized society by introducing renewable energybased electricity at our domestic and international sites.
Greenhouse gas emissions of Scope 1, 2 and 3
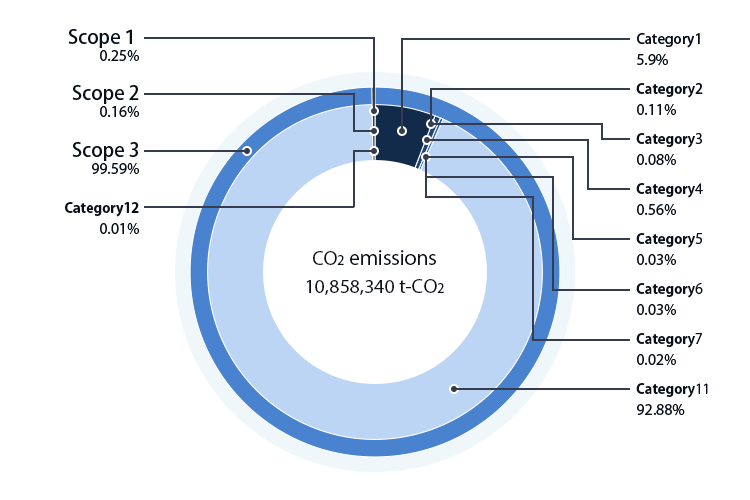
Scope1
| Emissions(t-CO2) | 26,867 |
|---|
Scope2
| Emissions(t-CO2) | 17,694 |
|---|
Scope3
| Emissions(t-CO2) | 10,813,779 |
|---|
| Category | Accounting methods* | Emissions amount(t-CO2) |
|---|---|---|
| Category 1: Purchased goods and services | Calculated from (raw) materials procurement amount (in value terms) | 638,480 |
| Category 2: Capital goods | Calculated from amount of capital investment | 12,228 |
| Category3: Fuel- and energy-related activities not included in Scope 1 or 2 | Calculated from purchased amount of electricity and fuels | 8,211 |
| Category4: Transportation and delivery (upstream) | Calculated from transportation costs accompanying procurement of (raw) materials | 60,718 |
| Category5: Waste generated in operations | Calculated from amount of waste discharged by type | 2,773 |
| Category6: Business travel | Calculated from travel expenses paid by mode of transportation | 2,999 |
| Category7: Employee commuting | Calculated from transportation expenses paid to employees | 1,852 |
| Category8: Leased assets (upstream) | included in Scope 1 and 2 emission calculation | ― |
| Category9: Transportation and delivery (downstream) | No relevant activities | ― |
| Category10: Processing of sold products | There are some products that are relevant, but calculations are ignored because their ratios in sales are extremely small. | ― |
| Category11: Use of sold products | Calculated from emissions from operation of facilities Taikisha provided, HFC leakage from equipment Taikisha provided, and estimated useful lives | 10,085,014 |
| Category12: End-of-life treatment of sold products | Calculated from weight of main equipment by type | 1,504 |
| Category13: Leased assets (downstream) | No relevant activities | ― |
| Category14: Franchises | No relevant activities | ― |
| Category15: Investments | Calculations are ignored because the validity of the category 15 estimates is low as a result of many portfolio companies not disclosing Scope 1 and 2 emissions and the impact of the category 15 estimates on the entire supply chain is small. | ― |
-
*Emission factor is calculated based on the Emission Factor Database on Accounting for Greenhouse Gas Emissions throughout the Supply Chain (ver.3.4) of the Ministry of the Environment and LCI Database IDEAv2 (for calculating greenhouse gas emissions in supply chain) of The National Institute of Advanced Industrial Science and Technology, Research Institute of Science for Safety and Sustainability, Advanced LCA Research Group, Sustainable Management Promotion Organization.
Total
| Total of Scope 1. 2 and 3 | 10,858,340 |
|---|
-
*CO2 emissions are calculated based on the GHG protocol.
